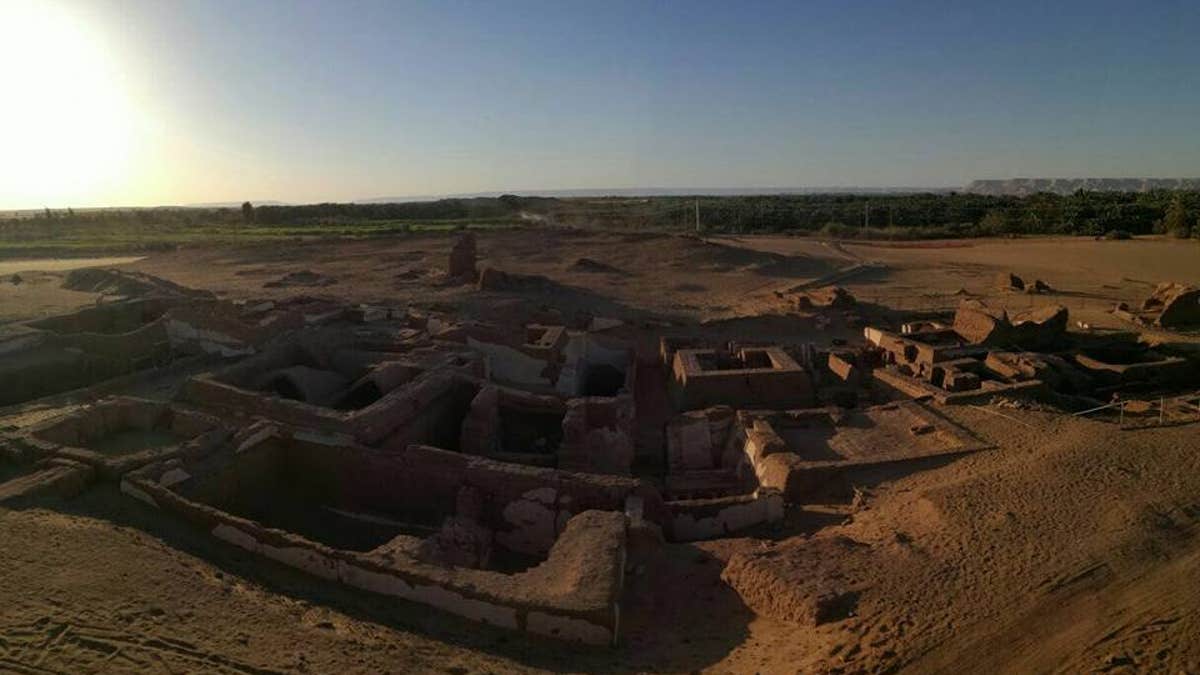
A series of Egyptian tombs dating back about 2,000 years, to the time when the Romans controlled Egypt, have been discovered at Bir esh-Shaghala in the Dakhla Oasis in Egypt. (Egypt Ministry of Antiquities)
A series of tombs dating back about 2,000 years, to the time when the Romans controlled Egypt, has been discovered, the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities announced Aug. 23.
Excavations at Bir esh-Shaghala in the Dakhla Oasis have uncovered tombs made of mudbrick and some are quite large containing multiple burial chambers. Some of the tombs have vaulted roofs and one tomb has a roof built in the shape of a pyramid. [See Photos of the Newly Discovered Tombs]
Five of the tombs were recently discovered while eight more were found within the past six excavation seasons, ministry officials said in a statement.
Artifacts were found in the tombs, including mummy masks and pieces of inscribed pottery known as ostraca. Giant containers were also found that may have held wine or olive oil, although chemical tests will need to be done to confirm this. The discovery of the tombs was made by a team of archaeologists from Egypt's Ministry of Antiquities. The excavations at Bir esh-Shaghala are scheduled to continue.
The Romans took over Egypt in 30 B.C., following Cleopatra VII's suicide after her navy was destroyed by the Roman Emperor Octavian at the Battle of Actium. While the Roman emperors ruled Egypt from Rome, the Egyptians revered the emperors as pharaohs. Their traditional Egyptian funerary customs (including mummification) and religious practices continued until the Roman Empire adopted Christianity as its official religion during the fourth century A.D.
Located in the Western Desert, about 217 miles (350 kilometers) west of Luxor, the Dakhla Oasis contains a vast amount of archaeological remains that date from prehistoric to modern times. A number of settlements from the Roman era flourished in the Dakhla Oasis. In 2014, Live Science reported that one of the Roman era settlements in the oasis had yielded the remains of an ancient school covered with writing that included references to drug use.
Original article on Live Science.