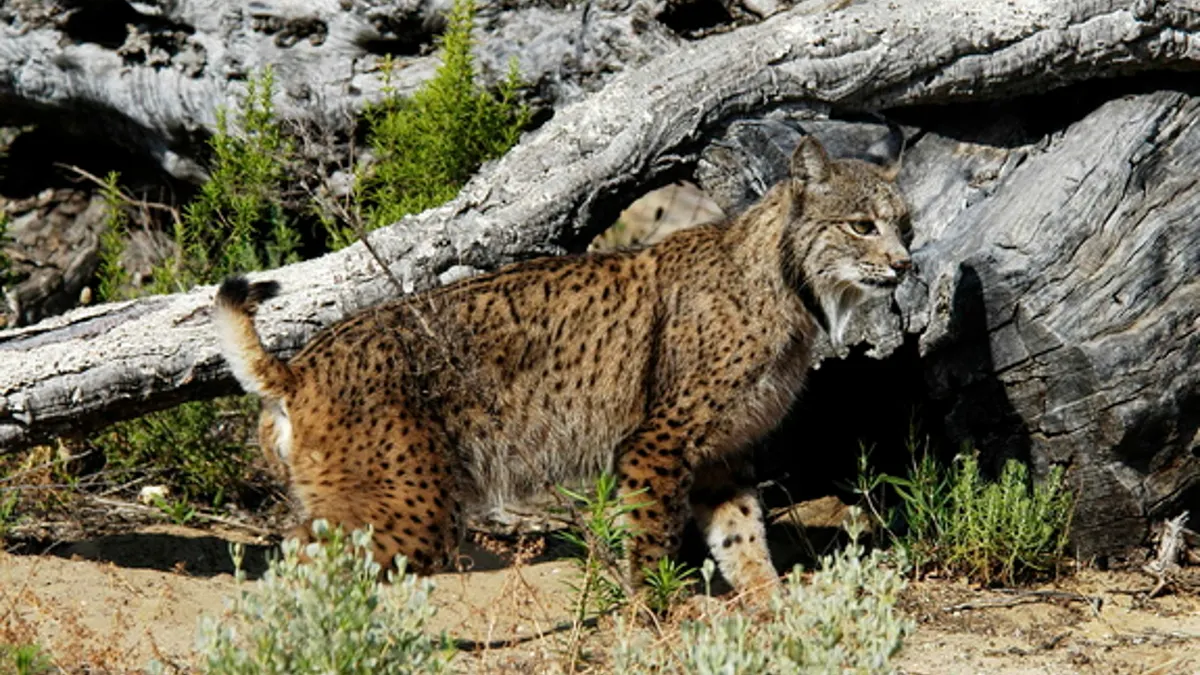
The Iberian lynx is the most endangered wild cat species worldwide. (Iberian Lynx Conservation Breeding Program)
It seems counterintuitive that castration could help save a species facing extinction.
But by removing the ovaries of a female Iberian lynx, scientists say they were able to collect and preserve embryos from the world's most endangered wild cat for the first time.
Conservationists are hoping the fertilized eggs could be implanted into a surrogate mother of a closely related species, possibly a Eurasian lynx female. Even one successful surrogate pregnancy could be a boost for felines, whose declining population had been estimated to be less than 200 a decade ago.
One Iberian lynx named Azahar, which was part of a breeding program in Silves, Portugal, had problems giving birth and underwent two emergency Caesarean sections in two consecutive pregnancies. Conservationists decided that, for health reasons, they shouldn't try breeding Azahar again and the cat's ovaries were removed by castration.
But immediately after Azahar's castration surgery, scientists say they obtained embryos and ovarian pieces from the feline in a process adapted from one used on domestic cats. [Feline Fun! 10 Amazing Facts About Cats]
"Seven days after mating we expected to flush embryos from the uterus," Katarina Jewgenow, a specialist from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (IZW) in Berlin, said in a statement. But instead, the oocytes (unfertilized eggs) and embryos had to be flushed out of the oviducts. This told the team something new about Iberian lynxes — their embryos develop more slowly than those of domestic cats.
The group of specialists also intervened when scientists decided to castrate a female Iberian lynx in captivity in Doñana, Spain. Named Saliega, this cat was relatively old (12 years), already gave birth to 16 cubs, and developed a mammary tumor last summer after her last lactating period.
"From her we only flushed unfertilized eggs, thus the male was not fertile," Natalia Mikolaewska, an IZW doctoral student, said in a statement. But the team was at least able to recover and freeze those oocytes, which could later be fertilized and implanted in a surrogate.
"The next step we are discussing right now is to implant these embryos into a foster mother, which might be an Eurasian lynx female," said Jewgenow.
The Iberian lynx is the only wild cat to be listed as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and IZW is working with the Iberian lynx Conservation Breeding Program to help save them.
If reviving a dying species sounds ambitious, consider the scientists who are trying to bring back animals that are already extinct. Biologists did actually resurrect the extinct Pyrenean ibex in 2003 by creating a clone from a frozen tissue sample harvested before the goat's entire population vanished in 2000. But that clone only survived for a few minutes after birth.
Researchers gathered in Washington, D.C., on March 15 for a forum called TEDxDeExtinction, hosted by the National Geographic Society, to dive into some of the practical and ethical questions surrounding current efforts to revive animals that have been dead for much longer than the Pyrenean ibex, such as the passenger pigeon and woolly mammoth.
Copyright 2013 LiveScience, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.