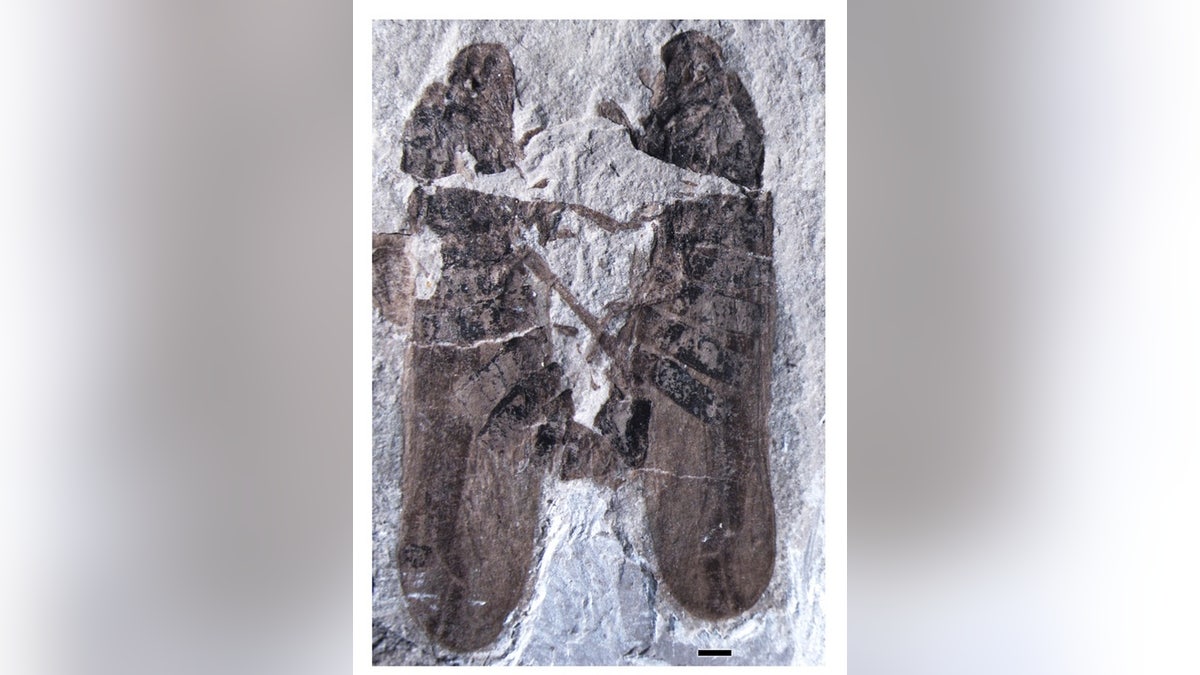
A fossil of two ancient insects in a love clinch has been unearthed in China. The fossil is the oldest example of insect sex ever found. (Su Li and Chungkun Shih)
About 165 million years ago Bam! froghoppers' mating session was interrupted by a volcanic eruption.
Now, scientists have unearthed a fossil in China that shows the two creatures immortalized in the act. The discovery, detailed Nov. 6 in the journal PLOS ONE, is the earliest fossil of insect sex ever discovered. It reveals that, at least for a group of sap-sucking insects called froghoppers, sex hasn't changed much over the last 165 million years.
Rare finds
Fossils of insects copulating usually trapped in amber are fairly rare, with only about 40 found around the world known to date, said study co-author Chung Kun Shih, a visiting professor from Capital Normal University in China. But until now, the oldest fossil showing insect sex dated to about 100 million years ago. [See Photos of Fossilized Turtles Caught in the Act]
[pullquote]
The researchers were excavating a fossil-rich area of Inner Mongolia in China when they discovered the two creatures clinging to each other.
In this region, "insect fossils are so good we can see the detailed structure, including the hair," Shih said.
The insects, of the species Anthoscytina perpetua, are face-to-face, with the male's sex organ, called the aedeagus, clearly inserted into the female's sex organ, called the bursa copulatrix.
"The male and female organ we can see it," Shih told LiveScience. "That's really rare."
The fossils dated to the middle Jurassic Period, about 165 million years ago. [See Images of the Fossil Insects Getting Busy]
Same old sex
Despite 165 million years having passed, modern-day froghoppers look anatomically very similar to the Jurassic insects, with symmetric sex organs.
Froghopper sex hasn't changed much in those 165 million years, either. The fossilized male's abdominal section is twisted in order to better insert his sex organ a position also seen in modern insect species. Froghoppers today also prefer to mate either face-to-face, when standing on a small twig or side by side on a leaf or tree trunk.
The team hypothesizes that the two insects were in a lover's hug when a volcanic eruption released a plume of poisonous gas, killing all life in the area, including the bacteria and fungus that would have normally decomposed their bodies. Later, wind or other natural forces tossed the love bugs into a nearby lake, where they were buried under layers of sediment and protected for millions of years.
The team isn't sure whether the insects were truly face-to-face during sex or were originally side by side and later shifted by natural forces after they died.
Copyright 2013 LiveScience, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.