The sun's magnetic field is gearing up to shift, a once in 11 year event, according to NASA officials. (NASA)
The sun is gearing up for a major solar flip, NASA says.
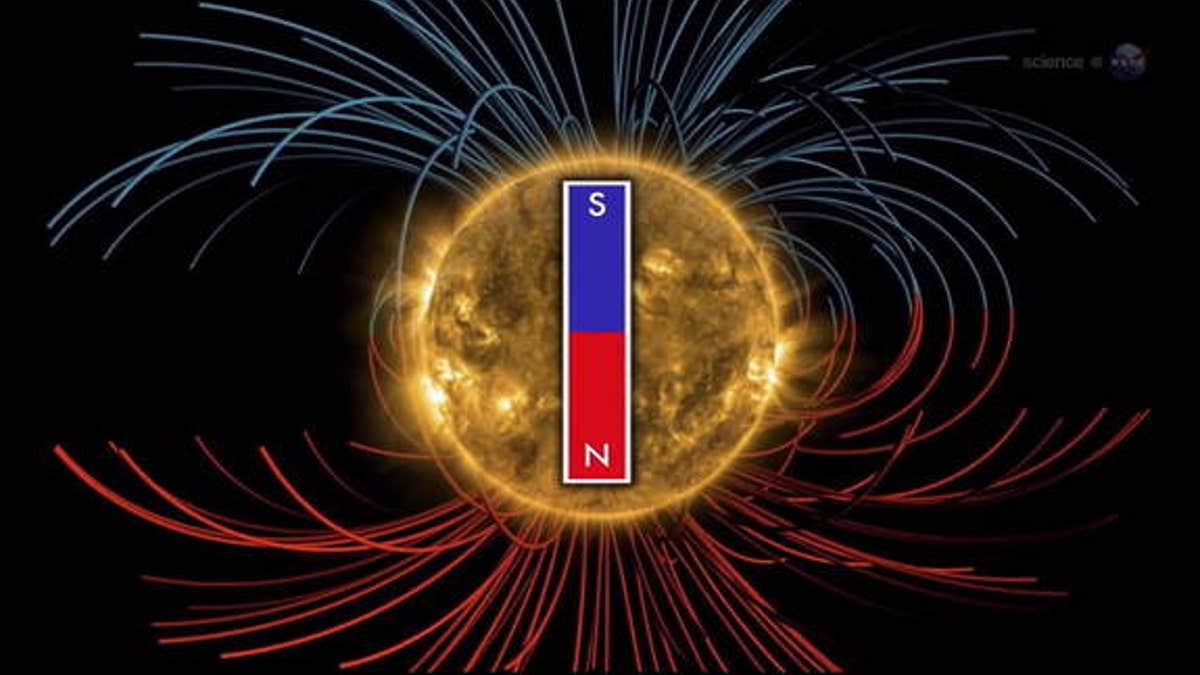
In an event that occurs once every 11 years, the magnetic field of the sun will change its polarity in a matter of months, according new observations by NASA-supported observatories.
The flipping of the sun's magnetic field marks the peak of the star's 11-year solar cycle and the halfway point in the sun's "solar maximum" — the peak of its solar weather cycle. NASA released a new video describing the sun's magnetic flip.
[pullquote]
"It looks like we're no more than three to four months away from a complete field reversal," Todd Hoeksema, the director of Stanford University's Wilcox Solar Observatory, said in a statement. "This change will have ripple effects throughout the solar system."
As the field shifts, the "current sheet" — a surface that radiates billions of kilometers outward from the sun's equator — becomes very wavy, NASA officials said. Earth orbits the sun, dipping in and out of the waves of the current sheet. The transition from a wave to a dip can create stormy space weather around Earth, NASA officials said.
"The sun's polar magnetic fields weaken, go to zero, and then emerge again with the opposite polarity," Stanford solar physicist Phil Scherrer said in a statement. "This is a regular part of the solar cycle."
While the polarity shift can stir up some stormy weather, it also provides extra shielding from dangerous cosmic rays. These high-energy particles, which are accelerated by events like supernova explosions, zip through the universe at nearly the speed of light. They can harm satellites and astronauts in space, and the wrinkled current sheet better protects the planet from these particles.
The effects of the rippled sheet can also be felt throughout the solar system, far beyond Pluto and even touching the Voyager probes near the barrier of interstellar space.
"The sun's north pole has already changed sign, while the south pole is racing to catch up," Scherrer said. "Soon, however, both poles will be reversed, and the second half of solar max will be underway."
The current solar maximum is the weakest in 100 years, experts have said. Usually, at the height of a solar cycle, sunspot activity increases. These dark regions on the sun's surface can give birth to solar flares and ejections, but there have been fewer observed sunspots this year than in the maximums of previous cycles.



















