NASA, SpaceX launch Crew-6 to International Space Station
SpaceX has launched four astronauts to the International Space Station for NASA. (Video: NASA TV)
NASA’s Curiosity rover captured and transmitted images of "sun rays" as the sun dropped below the horizon on Mars last month, which was part of a new cloud-imaging campaign that the rover is part of.
According to NASA, Martian sunsets can be "uniquely moody," which is what makes these new images unique.
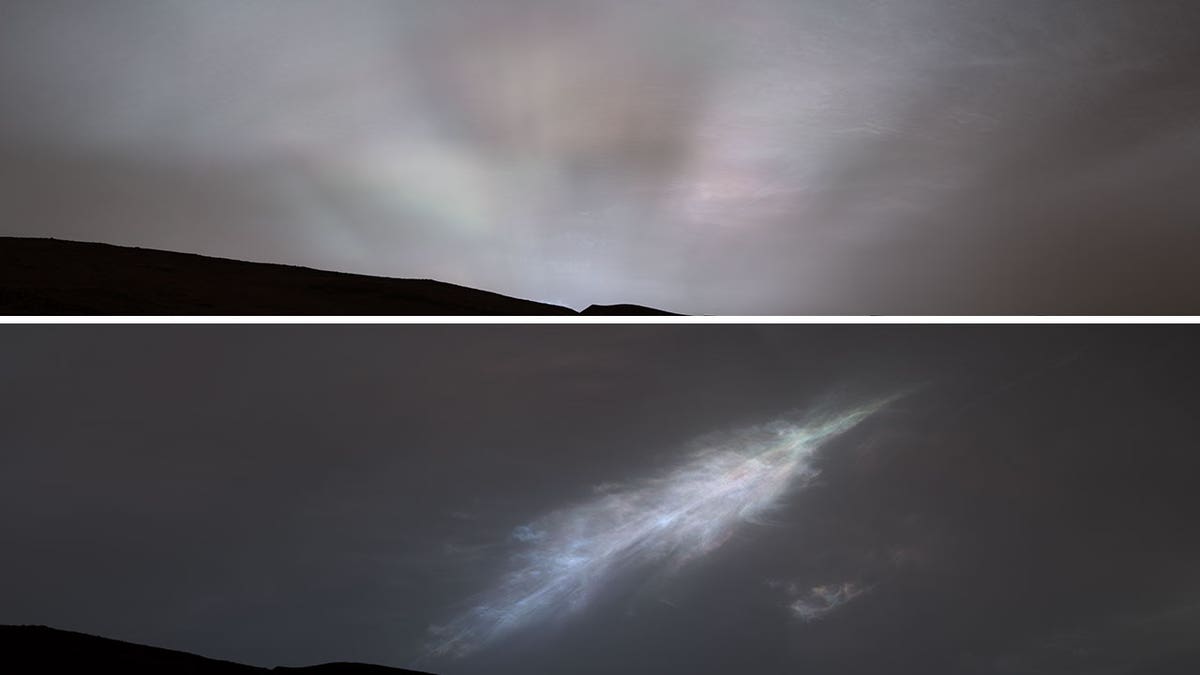

The Mars Curiosity rover sent back images of clouds in color, with the top image including sun rays and the bottom including a feather-shaped iridescent cloud. (NASA)
The "sun rays" were captured in an illuminated bank of clouds, and this was the first time NASA scientists had seen them so clearly on Mars.
CURIOSITY MARS ROVER FINDS THE ‘BEST EVIDENCE’ OF ANCIENT WATER IN RIPPLED ROCKS
NASA’s cloud-imaging campaign builds on 2021 observations of night-shining clouds, the space agency said, and while most clouds on Mars hover no more than 37 miles above the surface of the planet and are made of water ice, the clouds in the images sent from the rover appear to be at a higher and colder altitude.
Because the clouds are higher, scientists say they could be made of carbon dioxide ice, or dry ice.
In late January, the rover captured a feather-shaped iridescent cloud after sunset, which was also part of the cloud study.

The Curiosity Rover in a selfie taken on Martian Sol 2082 -June 15, 2018 Earth time. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
The feather-shaped cloud image is composed of 28 images captured with the rover’s mast camera, or Mastcam. The images were processed to put emphasis on the highlights, NASA said.
NASA CAPTURES PHOTO OF 'BEAR'S FACE' ON THE SURFACE OF MARS
Scientists hope that by studying where and when clouds form on Mars, they will get a better understanding about the composition of the planet’s atmosphere, including the temperatures and winds within it.
A cloud survey conducted in 2021 included images from the black-and-white navigation cameras and provided a look at the structure of clouds as they moved.
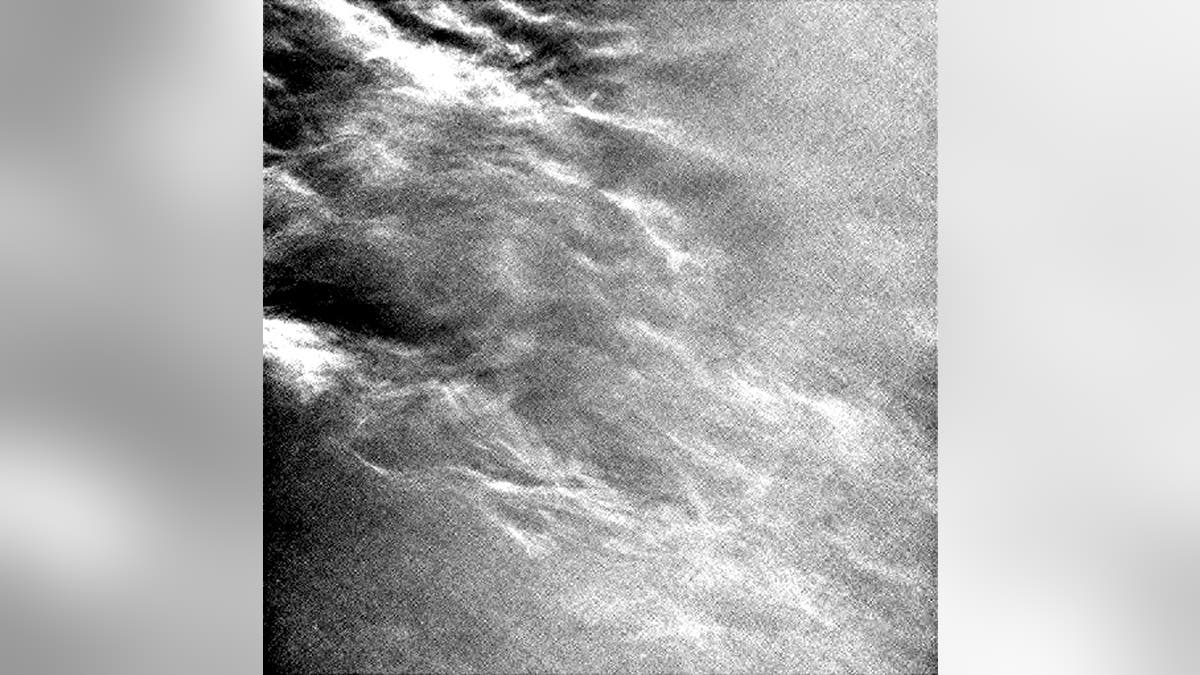
NASA's Curiosity rover captured images of cirrus clouds on July 17, 2017. (NASA)
The difference with this study is the Mastcam is providing color images, which show how the cloud particles grow over time, according to NASA.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
"Where we see iridescence, it means a cloud’s particle sizes are identical to their neighbors in each part of the cloud," Mark Lemmon, an atmospheric scientist with the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado said in a press release from NASA. "By looking at color transitions, we’re seeing particle size changing across the cloud. That tells us about the way the cloud is evolving and how its particles are changing size over time."
The Curiosity rover was launched on Nov. 26, 2011 and landed on Mars on Aug. 5, 2012. Its mission was to find out whether Mars ever had the right environmental conditions to support life, and early on, the rover discovered chemical and mineral evidence habitable environments from the past.









































