Monkeypox: What you need to know
Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security senior scholar says what people should do if they contract the virus on ‘Special Report.’
Monkeypox has been on the public’s radar after news broke out that a British resident tested positive for the rare virus on May 6, 2022.
While health experts have said that most people shouldn’t be at risk if they’ve stayed up to date on their smallpox vaccine, many can’t help but wonder about the current monkeypox outbreak while the COVID-19 pandemic still has its hold on the world.
Monkeypox symptoms include fever, muscle aches, exhaustion, headache, backache, the swelling of lymph nodes, chills and within one to three days, rash and lesions, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Here are quick, number-based facts about monkeypox.
MONKEYPOX PRESENTS MODERATE RISK TO GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH, WHO SAYS
1958 – Researchers first discovered monkeypox in 1958 after two outbreaks were observed in monkey colonies that were kept for studies, according to the CDC. The monkeys in question showed signs of a "pox-like disease," which led to the virus’ primate-referencing name.
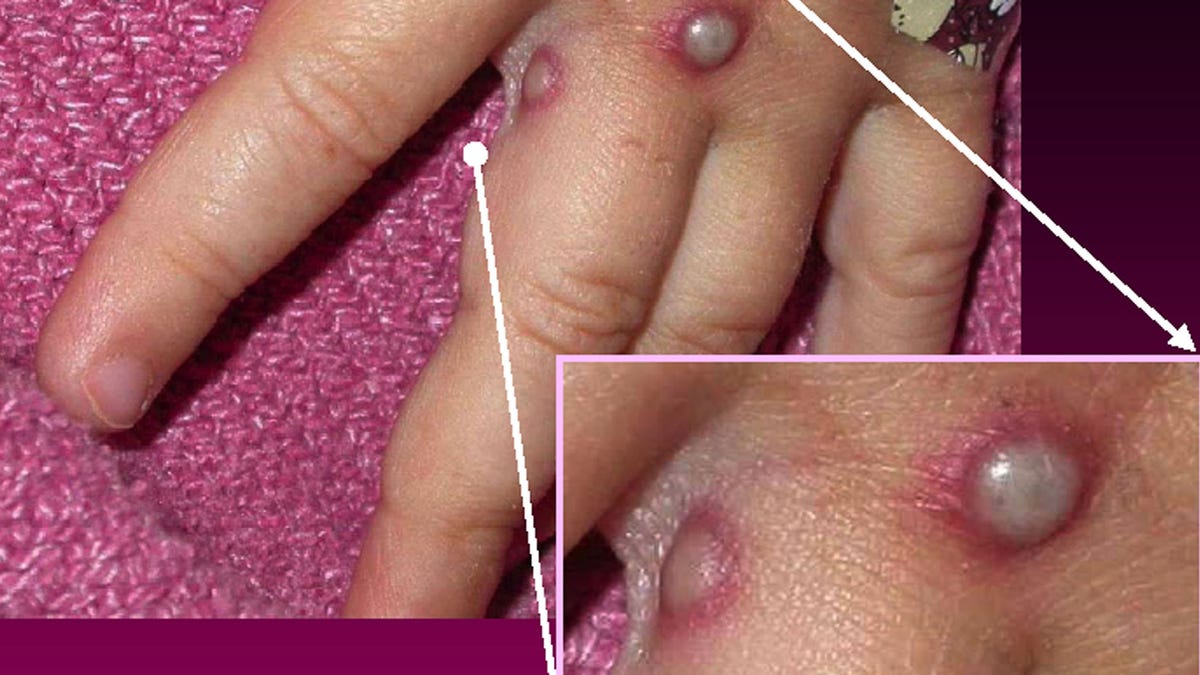
In this handout graphic from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, symptoms of the monkeypox virus are shown on a patient's hand on May 27, 2003. The CDC said the viral disease monkeypox, thought to be spread by prairie dogs, has been detected in the Americas for the first time with about 20 cases reported in Wisconsin, Illinois and Indiana. (Courtesy of CDC/Getty Images)
1970 – The first recorded case of a human monkeypox infection was in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, according to the CDC.
9 – In Africa, monkeypox has been found in nine countries in the continent’s central and western regions, including Cameroon, Central African Republic, Cote d’Ivoire, Gabon, Liberia, Nigeria, Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The CDC reports that monkeypox cases found outside of Africa have been "linked to international travel or imported animals."
WHO: NEARLY 200 CASES OF MONKEYPOX VIRUS ACROSS MORE THAN 20 COUNTRIES
6 – Six nations in Africa are currently experiencing a monkeypox endemic, according to data from the World Health Organization (WHO) As of May 26, the endemic countries include Cameroon (25 cases, 9 deaths), Central African Republic (8 cases, 2 deaths), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (1,284 cases, 58 deaths), Nigeria (46 cases, 0 deaths) and Republic of the Congo (2 cases, 0 deaths).
21 – U.S. monkeypox cases rose to 21 as of June 3, according to the CDC, with four cases each in California and New York, three in Florida, two in Colorado and in Utah and one in the states of Georgia, Illinois, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, Virginia and Washington.
In this illustration taken on May 22, 2022, test tubes labeled 'Monkeypox Virus Positive' are on display in a case. (REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration)
WHO: Non-endemic monkeypox countries
Eastern Mediterranean: United Arab Emirates and Sudan
Europe: Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, Finland France, Germany, Israel, Italy, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and U.K.
Pan America: Argentina, Canada, French Guiana and U.S.
Western Pacific: Australia
23 – Outside of Africa, the WHO received reports of confirmed monkeypox cases from 23 countries in the Eastern Mediterranean, Europe, Pan America and the Western Pacific. The cases were reported from May 13 to May 26.
31 – As of June 3, the CDC reported confirmed cases monkeypox spread to more countries. The full list of 31 countries can be found on the agency's website. These numbers have not yet been reported by the WHO.
257 – The WHO has confirmed 257 monkeypox cases in non-endemic countries as of May 26.
MONKEYPOX CONTINUES TO PUZZLE SCIENTISTS AS IT SPREADS TO MORE COUNTRIES
117 to 127 – Suspected cases of monkeypox cases in non-endemic countries are between 117 and 127, as of May 26.
3% to 6% – The fatality ratio of monkeypox in "recent times" has ranged between 3% and 6%, according to the World Health Organization. Previously, it ranged from 0% to 11%, with young children having a higher risk of death.
In this illustration taken on May 25, 2022, a woman holds a mock-up vial labeled ‘Monkeypox Vaccine’ and inserts a medical syringe. (REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration)
2 – There are two licensed smallpox vaccines that can be used for monkeypox, according to the CDC. The vaccines are ACAM200, which is made by Sanofi Pasteur Biologics Co., and JYNNEOSTMc, which is made by Bavarian Nordic. The CDC says smallpox vaccines can be used to protect humans from monkeypox because the due to the two viruses are "closely related."
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
1980 – In 1980, the World Health Assembly declared smallpox an "eradicated" disease, according to the CDC.
Fox News' Julia Musto contributed to this report.





















